Effective July 1, 2024
Only Correct Answers Shown for Studying Purposes
To save or print a Microsoft Word document (DOCX) version click here
If you want a more detailed approach that will explain amateur radio in depth, I recommend the ARRL Extra Class License Manual for Ham Radio 13th Edition which is a complete study guide with the question pool to help you pass the Technician Class (or select whatever class you are studying for) Amateur Radio Exam.
SUBELEMENT E1 – COMMISSION RULES [6 Exam Questions – 6 Groups]
E1A Frequency privileges; signal frequency range; automatic message forwarding; stations aboard ships or aircraft; power restriction on 630- and 2200-meter bands
E1A01 (D) [97.305, 97.307(b)]
Why is it not legal to transmit a 3 kHz bandwidth USB signal with a carrier frequency of 14.348 MHz?
D. The upper 1 kHz of the signal is outside the 20-meter band
E1A02 (D) [97.301, 97.305]
When using a transceiver that displays the carrier frequency of phone signals, which of the following displayed frequencies represents the lowest frequency at which a properly adjusted LSB emission will be totally within the band?
D. 3 kHz above the lower band edge
E1A03 (C) [97.305, 97.307(b)]
What is the highest legal carrier frequency on the 20-meter band for transmitting a 2.8 kHz wide USB data signal?
C. 14.1472 MHz
E1A04 (C) [97.301, 97.305]
May an Extra class operator answer the CQ of a station on 3.601 MHz LSB phone?
C. No, the sideband components will extend beyond the edge of the phone band segment
E1A05 (C) [97.5]
Who must be in physical control of the station apparatus of an amateur station aboard any vessel or craft that is documented or registered in the United States?
C. Any person holding an FCC issued amateur license or who is authorized for alien reciprocal operation
E1A06 (B) [97.303(h)(1)]
What is the required transmit frequency of a CW signal for channelized 60 meter operation?
B. At the center frequency of the channel
E1A07 (C) [97.313(k)]
What is the maximum power permitted on the 2200-meter band?
C. 1 watt EIRP (equivalent isotropic radiated power)
E1A08 (B) [97.219]
If a station in a message forwarding system inadvertently forwards a message that is in violation of FCC rules, who is primarily accountable for the rules violation?
B. The control operator of the originating station
E1A09 (D) [97.313(l)]
Except in some parts of Alaska, what is the maximum power permitted on the 630-meter band?
D. 5 watts EIRP (equivalent isotropic radiated power)
E1A10 (A) [97.11]
If an amateur station is installed aboard a ship or aircraft, what condition must be met before the station is operated?
A. Its operation must be approved by the master of the ship or the pilot in command of the aircraft
E1A11 (B) [97.5]
What licensing is required when operating an amateur station aboard a US-registered vessel in international waters?
B. Any FCC-issued amateur license
E1B Station restrictions and special operations: restrictions on station location; general operating restrictions; spurious emissions; antenna structure restrictions; RACES operations
E1B01 (D) [97.3]
Which of the following constitutes a spurious emission?
D. An emission outside the signal’s necessary bandwidth that can be reduced or eliminated without affecting the information transmitted
E1B02 (A) [97.307(f)(2)]
Which of the following is an acceptable bandwidth for digital voice or slow-scan TV transmissions made on the HF amateur bands?
A. 3 kHz
E1B03 (A) [97.13]
Within what distance must an amateur station protect an FCC monitoring facility from harmful interference?
A. 1 mile
E1B04 (C) [97.303(b)]
What must the control operator of a repeater operating in the 70-centimeter band do if a radiolocation system experiences interference from that repeater?
C. Cease operation or make changes to the repeater that mitigate the interference
E1B05 (C) [97.3]
What is the National Radio Quiet Zone?
C. An area surrounding the National Radio Astronomy Observatory
E1B06 (A) [97.15]
Which of the following additional rules apply if you are erecting an amateur station antenna structure at a site at or near a public use airport?
A. You may have to notify the Federal Aviation Administration and register it with the FCC as required by Part 17 of the FCC rules
E1B07 (C) [97.15]
To what type of regulations does PRB-1 apply?
C. State and local zoning
E1B08 (D) [97.121]
What limitations may the FCC place on an amateur station if its signal causes interference to domestic broadcast reception, assuming that the receivers involved are of good engineering design?
D. The amateur station must avoid transmitting during certain hours on frequencies that cause the interference
E1B09 (C) [97.407]
Which amateur stations may be operated under RACES rules?
C. Any FCC-licensed amateur station certified by the responsible civil defense organization for the area served
E1B10 (A) [97.407]
What frequencies are authorized to an amateur station operating under RACES rules?
A. All amateur service frequencies authorized to the control operator
E1B11 (B) [97.15]
What does PRB-1 require of state and local regulations affecting amateur radio antenna size and structures?
B. Reasonable accommodations of amateur radio must be made
E1C Automatic and remote control; band-specific regulations; operating in and communicating with foreign countries; spurious emission standards; HF modulation index limit; band-specific rules
E1C01 (D) [97.303]
What is the maximum bandwidth for a data emission on 60 meters?
D. 2.8 kHz
E1C02 (C) [97.117]
Which of the following apply to communications transmitted to amateur stations in foreign countries?
C. Communications must be limited to those incidental to the purpose of the amateur service and remarks of a personal nature
E1C03 (B) [97.303(g)]
How long must an operator wait after filing a notification with the Utilities Technology Council (UTC) before operating on the 2200-meter or 630-meter band?
B. Operators may operate after 30 days, providing they have not been told that their station is within 1 kilometer of PLC systems using those frequencies
E1C04 (A)
What is an IARP?
A. A permit that allows US amateurs to operate in certain countries of the Americas
E1C05 (B) [97.221(c)(1), 97.115(c)]
Under what situation may a station transmit third party communications while being automatically controlled?
B. Only when transmitting RTTY or data emissions
E1C06 (C)
Which of the following is required in order to operate in accordance with CEPT rules in foreign countries where permitted?
C. You must have a copy of FCC Public Notice DA 16-1048
E1C07 (D) [97.303(g)]
What notifications must be given before transmitting on the 630- or 2200-meter bands?
D. Operators must inform the Utilities Technology Council (UTC) of their call sign and coordinates of the station
E1C08 (B) [97.213]
What is the maximum permissible duration of a remotely controlled station’s transmissions if its control link malfunctions?
B. 3 minutes
E1C09 (B) [97.307]
What is the highest modulation index permitted at the highest modulation frequency for angle modulation below 29.0 MHz?
B. 1.0
E1C10 (A) [97.307]
What is the maximum mean power level for a spurious emission below 30 MHz with respect to the fundamental emission?
A. – 43 dB
E1C11 (A) [97.5]
Which of the following operating arrangements allows an FCC-licensed US citizen to operate in many European countries, and amateurs from many European countries to operate in the US?
A. CEPT
E1C12 (D) [97.305(c)]
In what portion of the 630-meter band are phone emissions permitted?
D. The entire band
E1D Amateur Space and Earth stations; telemetry and telecommand rules; identification of balloon transmissions; one-way communications
E1D01 (A) [97.3]
What is the definition of telemetry?
A. One-way transmission of measurements at a distance from the measuring instrument
E1D02 (B) [97.211(b)]
Which of the following may transmit encrypted messages?
B. Telecommand signals from a space telecommand station
E1D03 (B) [97.3(a)(45)]
What is a space telecommand station?
B. An amateur station that transmits communications to initiate, modify, or terminate functions of a space station
E1D04 (A) [97.119(a)]
Which of the following is required in the identification transmissions from a balloon-borne telemetry station?
A. Call sign
E1D05 (D) [97.213(d)]
What must be posted at the location of a station being operated by telecommand on or within 50 kilometers of the Earth’s surface?
A. A photocopy of the station license
B. A label with the name, address, and telephone number of the station licensee
C. A label with the name, address, and telephone number of the control operator
D. All these choices are correct
E1D06 (A) [97.215(c)]
What is the maximum permitted transmitter output power when operating a model craft by telecommand?
A. 1 watt
E1D07 (A) [97.207]
Which of the following HF amateur bands include allocations for space stations?
A. 40 meters, 20 meters, 15 meters, and 10 meters
E1D08 (D) [97.207]
Which VHF amateur bands have frequencies authorized for space stations?
D. 2 meters
E1D09 (B) [97.207]
Which UHF amateur bands have frequencies authorized for space stations?
B. 70 centimeters and 13 centimeters
E1D10 (B) [97.211]
Which amateur stations are eligible to be telecommand stations of space stations, subject to the privileges of the class of operator license held by the control operator of the station?
B. Any amateur station so designated by the space station licensee
E1D11 (D) [97.209]
Which amateur stations are eligible to operate as Earth stations?
D. Any amateur station, subject to the privileges of the class of operator license held by the control operator
E1D12 (A) [97.207(e), 97.203(g)]
Which of the following amateur stations may transmit one-way communications?
A. A space station, beacon station, or telecommand station
E1E Volunteer examiner program: definitions; qualifications; preparation and administration of exams; reimbursement; accreditation; question pools; documentation requirements
E1E01 (A) [97.527]
For which types of out-of-pocket expenses do the Part 97 rules state that VEs and VECs may be reimbursed?
A. Preparing, processing, administering, and coordinating an examination for an amateur radio operator license
E1E02 (C) [97.523]
Who is tasked by Part 97 with maintaining the pools of questions for all US amateur license examinations?
C. The VECs
E1E03 (C) [97.521]
What is a Volunteer Examiner Coordinator?
C. An organization that has entered into an agreement with the FCC to coordinate, prepare, and administer amateur operator license examinations
E1E04 (D) [97.509, 97.525]
What is required to be accredited as a Volunteer Examiner?
D. A VEC must confirm that the VE applicant meets FCC requirements to serve as an examiner
E1E05 (B) [97.509(j)]
What must the VE team do with the application form if the examinee does not pass the exam?
B. Return the application document to the examinee
E1E06 (C) [97.509]
Who is responsible for the proper conduct and necessary supervision during an amateur operator license examination session?
C. Each administering VE
E1E07 (B) [97.509, 97.511]
What should a VE do if a candidate fails to comply with the examiner’s instructions during an amateur operator license examination?
B. Immediately terminate the candidate’s examination
E1E08 (C) [97.509]
To which of the following examinees may a VE not administer an examination?
C. Relatives of the VE as listed in the FCC rules
E1E09 (A) [97.509]
What may be the penalty for a VE who fraudulently administers or certifies an examination?
A. Revocation of the VE’s amateur station license grant and the suspension of the VE’s amateur operator license grant
E1E10 (C) [97.509(m)]
What must the administering VEs do after the administration of a successful examination for an amateur operator license?
C. They must submit the application document to the coordinating VEC according to the coordinating VEC instructions
E1E11 (B) [97.509(i)]
What must the VE team do if an examinee scores a passing grade on all examination elements needed for an upgrade or new license?
B. Three VEs must certify that the examinee is qualified for the license grant and that they have complied with the administering VE requirements
E1F Miscellaneous rules: external RF power amplifiers; prohibited communications; spread spectrum; auxiliary stations; Canadian amateurs operating in the US; special temporary authority
E1F01 (B) [97.305]
On what frequencies are spread spectrum transmissions permitted?
B. Only on amateur frequencies above 222 MHz
E1F02 (C) [97.107]
What privileges are authorized in the US to persons holding an amateur service license granted by the government of Canada?
C. The operating terms and conditions of the Canadian amateur service license, not to exceed US Amateur Extra class license privileges
E1F03 (D) [97.315]
Under what circumstances may a dealer sell an external RF power amplifier capable of operation below 144 MHz if it has not been granted FCC certification?
D. The amplifier is constructed or modified by an amateur radio operator for use at an amateur station
E1F04 (A) [97.3]
Which of the following geographic descriptions approximately describes “Line A”?
A. A line roughly parallel to and south of the border between the US and Canada
E1F05 (D) [97.303]
Amateur stations may not transmit in which of the following frequency segments if they are located in the contiguous 48 states and north of Line A?
D. 420 MHz – 430 MHz
E1F06 (A) [1.931]
Under what circumstances might the FCC issue a Special Temporary Authority (STA) to an amateur station?
C. To allow a VE group with less than three VEs to administer examinations in a remote, sparsely populated area
E1F07 (D) [97.113]
When may an amateur station send a message to a business?
D. When neither the amateur nor their employer has a pecuniary interest in the communications
E1F08 (A) [97.113(c)]
Which of the following types of amateur station communications are prohibited?
A. Communications transmitted for hire or material compensation, except as otherwise provided in the rules
E1F09 (C) [FCC Part 97.113(a)(4)]
Which of the following cannot be transmitted over an amateur radio mesh network?
C. Messages encoded to obscure their meaning
E1F10 (B) [97.201]
Who may be the control operator of an auxiliary station?
B. Only Technician, General, Advanced, or Amateur Extra class operators
E1F11 (D) [97.317]
Which of the following best describes one of the standards that must be met by an external RF power amplifier if it is to qualify for a grant of FCC certification?
D. It must satisfy the FCC’s spurious emission standards when operated at the lesser of 1500 watts or its full output power
SUBELEMENT E2 – OPERATING PROCEDURES [5 Exam Questions – 5 Groups]
E2A Amateur radio in space: amateur satellites; orbital mechanics; frequencies and modes; satellite hardware; satellite operations
E2A01 (C)
What is the direction of an ascending pass for an amateur satellite?
C. From south to north
E2A02 (D)
Which of the following is characteristic of an inverting linear transponder?
A. Doppler shift is reduced because the uplink and downlink shifts are in opposite directions
B. Signal position in the band is reversed
C. Upper sideband on the uplink becomes lower sideband on the downlink, and vice versa
D. All these choices are correct
E2A03 (D)
How is an upload signal processed by an inverting linear transponder?
D. The signal is mixed with a local oscillator signal and the difference product is transmitted
E2A04 (B)
What is meant by the “mode” of an amateur radio satellite?
B. The satellite’s uplink and downlink frequency bands
E2A05 (D)
What do the letters in a satellite’s mode designator specify?
D. The uplink and downlink frequency ranges
E2A06 (A)
What are Keplerian elements?
A. Parameters that define the orbit of a satellite
E2A07 (D)
Which of the following types of signals can be relayed through a linear transponder?
A. FM and CW
B. SSB and SSTV
C. PSK and packet
D. All these choices are correct
E2A08 (B)
Why should effective radiated power (ERP) be limited to a satellite that uses a linear transponder?
B. To avoid reducing the downlink power to all other users
E2A09 (A)
What do the terms “L band” and “S band” specify?
A. The 23- and 13-centimeter bands
E2A10 (B)
What type of satellite appears to stay in one position in the sky?
B. Geostationary
E2A11 (B)
What type of antenna can be used to minimize the effects of spin modulation and Faraday rotation?
B. A circularly polarized antenna
E2A12 (C)
What is the purpose of digital store-and-forward functions on an amateur radio satellite?
C. To hold digital messages in the satellite for later download
E2B Television practices: fast-scan television standards and techniques; slow scan television standards and techniques
E2B01 (A)
In digital television, what does a coding rate of 3/4 mean?
A. 25% of the data sent is forward error correction data
E2B02 (C)
How many horizontal lines make up a fast-scan (NTSC) television frame?
C. 525
E2B03 (D)
How is an interlaced scanning pattern generated in a fast-scan (NTSC) television system?
D. By scanning odd-numbered lines in one field and even-numbered lines in the next
E2B04 (A)
How is color information sent in analog SSTV?
A. Color lines are sent sequentially
E2B05 (C)
Which of the following describes the use of vestigial sideband in analog fast-scan TV transmissions?
C. Vestigial sideband reduces the bandwidth while increasing the fidelity of low frequency video components
E2B06 (A)
What is vestigial sideband modulation?
A. Amplitude modulation in which one complete sideband and a portion of the other are transmitted
E2B07 (B)
Which types of modulation are used for amateur television DVB-T signals?
B. QAM and QPSK
E2B08 (A)
What technique allows commercial analog TV receivers to be used for fast-scan TV operations on the 70-centimeter band?
A. Transmitting on channels shared with cable TV
E2B09 (D)
What kind of receiver can be used to receive and decode SSTV using the Digital Radio Mondiale (DRM) protocol?
D. SSB
E2B10 (A)
What aspect of an analog slow-scan television signal encodes the brightness of the picture?
A. Tone frequency
E2B11 (B)
What is the function of the vertical interval signaling (VIS) code sent as part of an SSTV transmission?
B. To identify the SSTV mode being used
E2B12 (A)
What signals SSTV receiving software to begin a new picture line?
A. Specific tone frequencies
E2C Contest and DX operating; remote operation techniques; log data format; contact confirmation; RF network systems
E2C01 (D)
What indicator is required to be used by US-licensed operators when operating a station via remote control and the remote transmitter is located in the US?
D. No additional indicator is required
E2C02 (C)
Which of the following file formats is used for exchanging amateur radio log data?
C. ADIF
E2C03 (A)
From which of the following bands is amateur radio contesting generally excluded?
A. 30 meters
E2C04 (B)
Which of the following frequencies can be used for amateur radio mesh networks?
B. Frequencies shared with various unlicensed wireless data services
E2C05 (B)
What is the function of a DX QSL Manager?
B. Handle the receiving and sending of confirmations for a DX station
E2C06 (C)
During a VHF/UHF contest, in which band segment would you expect to find the highest level of SSB or CW activity?
C. In the weak signal segment of the band, with most of the activity near the calling frequency
E2C07 (A)
What is the Cabrillo format?
A. A standard for submission of electronic contest logs
E2C08 (D)
Which of the following contacts may be confirmed through the Logbook of The World (LoTW)?
A. Special event contacts between stations in the US
B. Contacts between a US station and a non-US station
C. Contacts for Worked All States credit
D. All these choices are correct
E2C09 (C)
What type of equipment is commonly used to implement an amateur radio mesh network?
C. A wireless router running custom firmware
E2C10 (D)
Why do DX stations often transmit and receive on different frequencies?
A. Because the DX station may be transmitting on a frequency that is prohibited to some responding stations
B. To separate the calling stations from the DX station
C. To improve operating efficiency by reducing interference
D. All these choices are correct
E2C11 (A)
How should you generally identify your station when attempting to contact a DX station during a contest or in a pileup?
A. Send your full call sign once or twice
E2C12 (C)
What indicates the delay between a control operator action and the corresponding change in the transmitted signal?
C. Latency
E2D Operating methods: digital modes and procedures for VHF and UHF; APRS; EME procedures; meteor scatter procedures
E2D01 (B)
Which of the following digital modes is designed for meteor scatter communications?
B. MSK144
E2D02 (D)
What information replaces signal-to-noise ratio when using the FT8 or FT4 modes in a VHF contest?
D. Grid square
E2D03 (D)
Which of the following digital modes is designed for EME communications?
D. Q65
E2D04 (C)
What technology is used for real-time tracking of balloons carrying amateur radio transmitters?
C. APRS
E2D05 (B)
What is the characteristic of the JT65 mode?
B. Decodes signals with a very low signal-to-noise ratio
E2D06 (A)
Which of the following is a method for establishing EME contacts?
A. Time-synchronous transmissions alternating between stations
E2D07 (C)
What digital protocol is used by APRS?
C. AX.25
E2D08 (C)
What type of packet frame is used to transmit APRS beacon data?
C. Unnumbered Information
E2D09 (A)
What type of modulation is used by JT65?
A. Multitone AFSK
E2D10 (C)
What does the packet path WIDE3-1 designate?
C. Three digipeater hops are requested with one remaining
E2D11 (D)
How do APRS stations relay data?
D. By packet digipeaters
E2E Operating methods: digital modes and procedures for HF
E2E01 (B)
Which of the following types of modulation is used for data emissions below 30 MHz?
B. FSK
E2E02 (B)
Which of the following synchronizes WSJT-X digital mode transmit/receive timing?
B. Synchronization of computer clocks
E2E03 (B)
To what does the “4” in FT4 refer?
B. Four-tone continuous-phase frequency shift keying
E2E04 (D)
Which of the following is characteristic of the FST4 mode?
A. Four-tone Gaussian frequency shift keying
B. Variable transmit/receive periods
C. Seven different tone spacings
D. All these choices are correct
E2E05 (A)
Which of these digital modes does not support keyboard-to-keyboard operation?
A. WSPR
E2E06 (C)
What is the length of an FT8 transmission cycle?
C. 15 seconds
E2E07 (C)
How does Q65 differ from JT65?
C. Multiple receive cycles are averaged
E2E08 (B)
Which of the following HF digital modes can be used to transfer binary files?
B. PACTOR
E2E09 (D)
Which of the following HF digital modes uses variable-length character coding?
D. PSK31
E2E10 (C)
Which of these digital modes has the narrowest bandwidth?
C. FT8
E2E11 (A)
What is the difference between direct FSK and audio FSK?
A. Direct FSK modulates the transmitter VFO
E2E12 (A)
How do ALE stations establish contact?
A. ALE constantly scans a list of frequencies, activating the radio when the designated call sign is received
E2E13 (D)
Which of these digital modes has the highest data throughput under clear communication conditions?
D. PACTOR IV
SUBELEMENT E3 – RADIO WAVE PROPAGATION [3 Exam Questions – 3 Groups]
E3A Electromagnetic Waves and Specialized Propagation: Earth-Moon-Earth (EME) communications; meteor scatter; microwave tropospheric and scatter propagation; auroral propagation; daily variation of ionospheric propagation; circular polarization
E3A01 (D)
What is the approximate maximum separation measured along the surface of the Earth between two stations communicating by EME?
D. 12,000 miles, if the moon is “visible” by both stations
E3A02 (B)
What characterizes libration fading of an EME signal?
B. A fluttery, irregular fading
E3A03 (A)
When scheduling EME contacts, which of these conditions will generally result in the least path loss?
A. When the Moon is at perigee
E3A04 (D)
In what direction does an electromagnetic wave travel?
D. It travels at a right angle to the electric and magnetic fields
E3A05 (C)
How are the component fields of an electromagnetic wave oriented?
C. They are at right angles
E3A06 (B)
What should be done to continue a long-distance contact when the MUF for that path decreases due to darkness?
B. Switch to a lower frequency HF band
E3A07 (C)
Atmospheric ducts capable of propagating microwave signals often form over what geographic feature?
C. Large bodies of water
E3A08 (A)
When a meteor strikes the Earth’s atmosphere, a linear ionized region is formed at what region of the ionosphere?
A. The E region
E3A09 (C)
Which of the following frequency ranges is most suited for meteor-scatter communications?
C. 28 MHz – 148 MHz
E3A10 (D)
What determines the speed of electromagnetic waves through a medium?
D. The index of refraction
E3A11 (B)
What is a typical range for tropospheric duct propagation of microwave signals?
B. 100 miles to 300 miles
E3A12 (C)
What is most likely to result in auroral propagation?
C. Severe geomagnetic storms
E3A13 (A)
Which of these emission modes is best for auroral propagation?
A. CW
E3A14 (B)
What are circularly polarized electromagnetic waves?
B. Waves with rotating electric and magnetic fields
E3B Transequatorial propagation; long-path propagation; ordinary and extraordinary waves; chordal hop; sporadic-E mechanisms; ground-wave propagation
E3B01 (A)
Where is transequatorial propagation (TEP) most likely to occur?
A. Between points separated by 2,000 miles to 3,000 miles over a path perpendicular to the geomagnetic equator
E3B02 (C)
What is the approximate maximum range for signals using transequatorial propagation?
C. 5,000 miles
E3B03 (C)
At what time of day is transequatorial propagation most likely to occur?
C. Afternoon or early evening
E3B04 (B)
What are “extraordinary” and “ordinary” waves?
B. Independently propagating, elliptically polarized waves created in the ionosphere
E3B05 (D)
Which of the following paths is most likely to support long-distance propagation on 160 meters?
D. A path entirely in darkness
E3B06 (B)
On which of the following amateur bands is long-path propagation most frequent?
B. 40 meters and 20 meters
E3B07 (C)
What effect does lowering a signal’s transmitted elevation angle have on ionospheric HF skip propagation?
C. The distance covered by each hop increases
E3B08 (C)
How does the maximum range of ground-wave propagation change when the signal frequency is increased?
C. It decreases
E3B09 (A)
At what time of year is sporadic-E propagation most likely to occur?
A. Around the solstices, especially the summer solstice
E3B10 (A)
What is the effect of chordal-hop propagation?
A. The signal experiences less loss compared to multi-hop propagation, which uses Earth as a reflector
E3B11 (D)
At what time of day is sporadic-E propagation most likely to occur?
D. Between sunrise and sunset
E3B12 (B)
What is chordal-hop propagation?
B. Successive ionospheric refractions without an intermediate reflection from the ground
E3B13 (A)
What type of polarization is supported by ground-wave propagation?
A. Vertical
E3C Propagation prediction and reporting: radio horizon; effects of space-weather phenomena
E3C01 (D)
What is the cause of short-term radio blackouts?
D. Solar flares
E3C02 (A)
What is indicated by a rising A-index or K-index?
A. Increasing disturbance of the geomagnetic field
E3C03 (B)
Which of the following signal paths is most likely to experience high levels of absorption when the A-index or K-index is elevated?
B. Through the auroral oval
E3C04 (C)
What does the value of Bz (B sub z) represent?
C. North-south strength of the interplanetary magnetic field
E3C05 (A)
What orientation of Bz (B sub z) increases the likelihood that charged particles from the Sun will cause disturbed conditions?
A. Southward
E3C06 (A)
How does the VHF/UHF radio horizon compare to the geographic horizon?
A. It is approximately 15 percent farther
E3C07 (D)
Which of the following indicates the greatest solar flare intensity?
D. Class X
E3C08 (D)
Which of the following is the space-weather term for an extreme geomagnetic storm?
D. G5
E3C09 (D)
What type of data is reported by amateur radio propagation reporting networks?
D. Digital-mode and CW signals
E3C10 (B)
What does the 304A solar parameter measure?
B. UV emissions at 304 angstroms, correlated to the solar flux index
E3C11 (C)
What does VOACAP software model?
C. HF propagation
E3C12 (B)
Which of the following is indicated by a sudden rise in radio background noise across a large portion of the HF spectrum?
B. A coronal mass ejection impact or a solar flare has occurred
SUBELEMENT E4 – AMATEUR PRACTICES [5 Exam Questions – 5 Groups]
E4A Test equipment: analog and digital instruments; spectrum analyzers; antenna analyzers; oscilloscopes; RF measurements
E4A01 (A)
Which of the following limits the highest frequency signal that can be accurately displayed on a digital oscilloscope?
A. Sampling rate of the analog-to-digital converter
E4A02 (B)
Which of the following parameters does a spectrum analyzer display on the vertical and horizontal axes?
B. Signal amplitude and frequency
E4A03 (B)
Which of the following test instruments is used to display spurious signals and/or intermodulation distortion products generated by an SSB transmitter?
B. Spectrum analyzer
E4A04 (A)
How is compensation of an oscilloscope probe performed?
A. A square wave is displayed, and the probe is adjusted until the horizontal portions of the displayed wave are as nearly flat as possible
E4A05 (D)
What is the purpose of using a prescaler with a frequency counter?
D. Reduce the signal frequency to within the counter’s operating range
E4A06 (A)
What is the effect of aliasing on a digital oscilloscope when displaying a waveform?
A. A false, jittery low-frequency version of the waveform is displayed
E4A07 (B)
Which of the following is an advantage of using an antenna analyzer compared to an SWR bridge?
B. Antenna analyzers compute SWR and impedance automatically
E4A08 (D)
Which of the following is used to measure SWR?
A. Directional wattmeter
B. Vector network analyzer
C. Antenna analyzer
D. All these choices are correct
E4A09 (A)
Which of the following is good practice when using an oscilloscope probe?
A. Minimize the length of the probe’s ground connection
E4A10 (D)
Which trigger mode is most effective when using an oscilloscope to measure a linear power supply’s output ripple?
D. Line
E4A11 (D)
Which of the following can be measured with an antenna analyzer?
A. Velocity factor
B. Cable length
C. Resonant frequency of a tuned circuit
D. All these choices are correct
E4B Measurement technique and limitations: instrument accuracy and performance limitations; probes; techniques to minimize errors; measurement of Q; instrument calibration; S parameters; vector network analyzers; RF signals
E4B01 (B)
Which of the following factors most affects the accuracy of a frequency counter?
B. Time base accuracy
E4B02 (A)
What is the significance of voltmeter sensitivity expressed in ohms per volt?
A. The full scale reading of the voltmeter multiplied by its ohms per volt rating is the input impedance of the voltmeter
E4B03 (C)
Which S parameter is equivalent to forward gain?
C. S21
E4B04 (A)
Which S parameter represents input port return loss or reflection coefficient (equivalent to VSWR)?
A. S11
E4B05 (B)
What three test loads are used to calibrate an RF vector network analyzer?
B. Short circuit, open circuit, and 50 ohms
E4B06 (D)
How much power is being absorbed by the load when a directional power meter connected between a transmitter and a terminating load reads 100 watts forward power and 25 watts reflected power?
D. 75 watts
E4B07 (A)
What do the subscripts of S parameters represent?
A. The port or ports at which measurements are made
E4B08 (C)
Which of the following can be used to determine the Q of a series-tuned circuit?
C. The bandwidth of the circuit’s frequency response
E4B09 (B)
Which of the following can be measured by a two-port vector network analyzer?
B. Filter frequency response
E4B10 (B)
Which of the following methods measures intermodulation distortion in an SSB transmitter?
B. Modulate the transmitter using two AF signals having non-harmonically related frequencies and observe the RF output with a spectrum analyzer
E4B11 (D)
Which of the following can be measured with a vector network analyzer?
A. Input impedance
B. Output impedance
C. Reflection coefficient
D. All these choices are correct
E4C Receiver performance: phase noise, noise floor, image rejection, minimum detectable signal (MDS), increasing signal-to-noise ratio and dynamic range, noise figure, reciprocal mixing; selectivity; SDR non-linearity; use of attenuators at low frequencies
E4C01 (D)
What is an effect of excessive phase noise in an SDR receiver’s master clock oscillator?
D. It can combine with strong signals on nearby frequencies to generate interference
E4C02 (A)
Which of the following receiver circuits can be effective in eliminating interference from strong out-of-band signals?
A. A front-end filter or preselector
E4C03 (C)
What is the term for the suppression in an FM receiver of one signal by another stronger signal on the same frequency?
C. Capture effect
E4C04 (D)
What is the noise figure of a receiver?
D. The ratio in dB of the noise generated by the receiver to the theoretical minimum noise
E4C05 (B)
What does a receiver noise floor of -174 dBm represent?
B. The theoretical noise in a 1 Hz bandwidth at the input of a perfect receiver at room temperature
E4C06 (D)
How much does increasing a receiver’s bandwidth from 50 Hz to 1,000 Hz increase the receiver’s noise floor?
D. 13 dB
E4C07 (B)
What does the MDS of a receiver represent?
A. The meter display sensitivityB. The minimum discernible signal
E4C08 (D)
An SDR receiver is overloaded when input signals exceed what level?
D. The reference voltage of the analog-to-digital converter
E4C09 (C)
Which of the following choices is a good reason for selecting a high IF for a superheterodyne HF or VHF communications receiver?
C. Easier for front-end circuitry to eliminate image responses
E4C10 (C)
What is an advantage of having a variety of receiver bandwidths from which to select?
C. Receive bandwidth can be set to match the modulation bandwidth, maximizing signal-to-noise ratio and minimizing interference
E4C11 (D)
Why does input attenuation reduce receiver overload on the lower frequency HF bands with little or no impact on signal-to-noise ratio?
D. Atmospheric noise is generally greater than internally generated noise even after attenuation
E4C12 (C)
How does a narrow-band roofing filter affect receiver performance?
C. It improves blocking dynamic range by attenuating strong signals near the receive frequency
E4C13 (D)
What is reciprocal mixing?
D. Local oscillator phase noise mixing with adjacent strong signals to create interference to desired signals
E4C14 (C)
What is the purpose of the receiver IF Shift control?
C. To reduce interference from stations transmitting on adjacent frequencies
E4D Receiver performance characteristics: dynamic range; intermodulation and cross-modulation interference; third-order intercept; desensitization; preselector; sensitivity; link margin
E4D01 (A)
What is meant by the blocking dynamic range of a receiver?
A. The difference in dB between the noise floor and the level of an incoming signal that will cause 1 dB of gain compression
E4D02 (A)
Which of the following describes problems caused by poor dynamic range in a receiver?
A. Spurious signals caused by cross modulation and desensitization from strong adjacent signals
E4D03 (B)
What creates intermodulation interference between two repeaters in close proximity?
B. The output signals mix in the final amplifier of one or both transmitters
E4D04 (B)
Which of the following is used to reduce or eliminate intermodulation interference in a repeater caused by a nearby transmitter?
B. A properly terminated circulator at the output of the repeater’s transmitter
E4D05 (A)
What transmitter frequencies would create an intermodulation-product signal in a receiver tuned to 146.70 MHz when a nearby station transmits on 146.52 MHz?
A. 146.34 MHz and 146.61 MHz
E4D06 (C)
What is the term for the reduction in receiver sensitivity caused by a strong signal near the received frequency?
C. Desensitization
E4D07 (A)
Which of the following reduces the likelihood of receiver desensitization?
A. Insert attenuation before the first RF stage
E4D08 (C)
What causes intermodulation in an electronic circuit?
C. Nonlinear circuits or devices
E4D09 (C)
What is the purpose of the preselector in a communications receiver?
C. To increase the rejection of signals outside the band being received
E4D10 (C)
What does a third-order intercept level of 40 dBm mean with respect to receiver performance?
C. A pair of 40 dBm input signals will theoretically generate a third-order intermodulation product that has the same output amplitude as either of the input signals
E4D11 (A)
Why are odd-order intermodulation products, created within a receiver, of particular interest compared to other products?
A. Odd-order products of two signals in the band being received are also likely to be within the band
E4D12 (C)
What is the link margin in a system with a transmit power level of 10 W (+40 dBm), a system antenna gain of 10 dBi, a cable loss of 3 dB, a path loss of 136 dB, a receiver minimum discernable signal of -103 dBm, and a required signal-to-noise ratio of 6 dB?
C. +8dB
E4D13 (A)
What is the received signal level with a transmit power of 10 W (+40 dBm), a transmit antenna gain of 6 dBi, a receive antenna gain of 3 dBi, and a path loss of 100 dB?
A. -51 dBm
E4D14 (D)
What power level does a receiver minimum discernible signal of -100 dBm represent?
D. 0.1 picowatts
E4E Noise and interference: external RF interference; electrical and computer noise; line noise; DSP filtering and noise reduction; common-mode current; surge protectors; single point ground panel
E4E01 (A)
What problem can occur when using an automatic notch filter (ANF) to remove interfering carriers while receiving CW signals?
A. Removal of the CW signal as well as the interfering carrier
E4E02 (D)
Which of the following types of noise can often be reduced by a digital noise reduction?
A. Broadband white noise
B. Ignition noise
C. Power line noise
D. All these choices are correct
E4E03 (B)
Which of the following types of noise are removed by a noise blanker?
B. Impulse noise
E4E04 (D)
How can conducted noise from an automobile battery charging system be suppressed?
D. By installing ferrite chokes on the charging system leads
E4E05 (B)
What is used to suppress radio frequency interference from a line-driven AC motor?
B. A brute-force AC-line filter in series with the motor’s power leads
E4E06 (C)
What type of electrical interference can be caused by computer network equipment?
C. The appearance of unstable modulated or unmodulated signals at specific frequencies
E4E07 (B)
Which of the following can cause shielded cables to radiate or receive interference?
B. Common-mode currents on the shield and conductors
E4E08 (B)
What current flows equally on all conductors of an unshielded multiconductor cable?
B. Common-mode current
E4E09 (C)
What undesirable effect can occur when using a noise blanker?
C. Strong signals may be distorted and appear to cause spurious emissions
E4E10 (D)
Which of the following can create intermittent loud roaring or buzzing AC line interference?
A. Arcing contacts in a thermostatically controlled device
B. A defective doorbell or doorbell transformer inside a nearby residence
C. A malfunctioning illuminated advertising display
D. All these choices are correct
E4E11 (B)
What could be the cause of local AM broadcast band signals combining to generate spurious signals on the MF or HF bands?
B. Nearby corroded metal connections are mixing and reradiating the broadcast signals
E4E12 (A)
What causes interference received as a series of carriers at regular intervals across a wide frequency range?
A. Switch-mode power supplies
E4E13 (C)
Where should a station AC surge protector be installed?
C. On the single point ground panel
E4E14 (D)
What is the purpose of a single point ground panel?
D. Ensure all lightning protectors activate at the same time
SUBELEMENT E5 – ELECTRICAL PRINCIPLES [4 Exam Questions – 4 Groups]
E5A Resonance and Q: characteristics of resonant circuits; series and parallel resonance; definitions and effects of Q; half-power bandwidth
E5A01 (A)
What can cause the voltage across reactances in a series RLC circuit to be higher than the voltage applied to the entire circuit?
A. Resonance
E5A02 (C)
What is the resonant frequency of an RLC circuit if R is 22 ohms, L is 50 microhenries, and C is 40 picofarads?
C. 3.56 MHz
E5A03 (D)
What is the magnitude of the impedance of a series RLC circuit at resonance?
D. Approximately equal to circuit resistance
E5A04 (A)
What is the magnitude of the impedance of a parallel RLC circuit at resonance?
A. Approximately equal to circuit resistance
E5A05 (A)
What is the result of increasing the Q of an impedance-matching circuit?
A. Matching bandwidth is decreased
E5A06 (B)
What is the magnitude of the circulating current within the components of a parallel LC circuit at resonance?
B. It is at a maximum
E5A07 (A)
What is the magnitude of the current at the input of a parallel RLC circuit at resonance?
A. Minimum
E5A08 (C)
What is the phase relationship between the current through and the voltage across a series resonant circuit at resonance?
C. The voltage and current are in phase
E5A09 (C)
How is the Q of an RLC parallel resonant circuit calculated?
C. Resistance divided by the reactance of either the inductance or capacitance
E5A10 (A)
What is the resonant frequency of an RLC circuit if R is 33 ohms, L is 50 microhenries, and C is 10 picofarads?
A. 7.12 MHz
E5A11 (C)
What is the half-power bandwidth of a resonant circuit that has a resonant frequency of 7.1 MHz and a Q of 150?
C. 47.3 kHz
E5A12 (C)
What is the half-power bandwidth of a resonant circuit that has a resonant frequency of 3.7 MHz and a Q of 118?
C. 31.4 kHz
E5A13 (C)
What is an effect of increasing Q in a series resonant circuit?
C. Internal voltages increase
E5B Time constants and phase relationships: RL and RC time constants; phase angle in reactive circuits and components; admittance and susceptance
E5B01 (B)
What is the term for the time required for the capacitor in an RC circuit to be charged to 63.2% of the applied voltage or to discharge to 36.8% of its initial voltage?
B. One time constant
E5B02 (D)
What letter is commonly used to represent susceptance?
D. B
E5B03 (B)
How is impedance in polar form converted to an equivalent admittance?
B. Take the reciprocal of the magnitude and change the sign of the angle
E5B04 (D)
What is the time constant of a circuit having two 220-microfarad capacitors and two 1-megohm resistors, all in parallel?
D. 220 seconds
E5B05 (D)
What is the effect on the magnitude of pure reactance when it is converted to susceptance?
D. It is replaced by its reciprocal
E5B06 (C)
What is susceptance?
C. The imaginary part of admittance
E5B07 (C)
What is the phase angle between the voltage across and the current through a series RLC circuit if XC is 500 ohms, R is 1 kilohm, and XL is 250 ohms?
C. 14.0 degrees with the voltage lagging the current
E5B08 (A)
What is the phase angle between the voltage across and the current through a series RLC circuit if XC is 300 ohms, R is 100 ohms, and XL is 100 ohms?
A. 63 degrees with the voltage lagging the current
E5B09 (D)
What is the relationship between the AC current through a capacitor and the voltage across a capacitor?
D. Current leads voltage by 90 degrees
E5B10 (A)
What is the relationship between the AC current through an inductor and the voltage across an inductor?
A. Voltage leads current by 90 degrees
E5B11 (B)
What is the phase angle between the voltage across and the current through a series RLC circuit if XC is 25 ohms, R is 100 ohms, and XL is 75 ohms?
B. 27 degrees with the voltage leading the current
E5B12 (A)
What is admittance?
A. The inverse of impedance
E5C Coordinate systems and phasors in electronics: rectangular coordinates; polar coordinates; phasors; logarithmic axes
E5C01 (A)
Which of the following represents pure capacitive reactance of 100 ohms in rectangular notation?
A. 0 – j100
E5C02 (C)
How are impedances described in polar coordinates?
C. By magnitude and phase angle
E5C03 (C)
Which of the following represents a pure inductive reactance in polar coordinates?
C. A positive 90 degree phase angle
E5C04 (D)
What type of Y-axis scale is most often used for graphs of circuit frequency response?
D. Logarithmic
E5C05 (C)
What kind of diagram is used to show the phase relationship between impedances at a given frequency?
C. Phasor diagram
E5C06 (B)
What does the impedance 50 – j25 ohms represent?
B. 50 ohms resistance in series with 25 ohms capacitive reactance
E5C07 (D)
Where is the impedance of a pure resistance plotted on rectangular coordinates?
D. On the horizontal axis
E5C08 (D)
What coordinate system is often used to display the phase angle of a circuit containing resistance, inductive, and/or capacitive reactance?
D. Polar coordinates
E5C09 (A)
When using rectangular coordinates to graph the impedance of a circuit, what do the axes represent?
A. The X axis represents the resistive component, and the Y axis represents the reactive component
E5C10 (B)
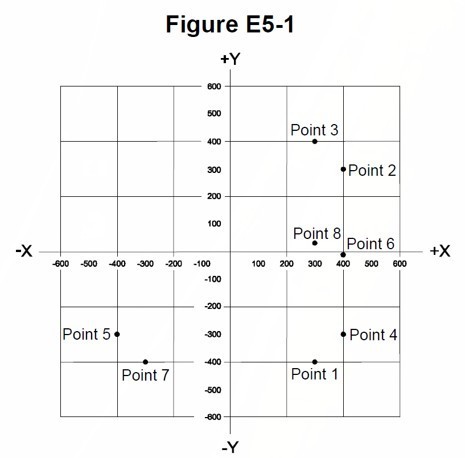
Which point on Figure E5-1 best represents the impedance of a series circuit consisting of a 400-ohm resistor and a 38-picofarad capacitor at 14 MHz?
B. Point 4
E5C11 (B)
Which point in Figure E5-1 best represents the impedance of a series circuit consisting of a 300-ohm resistor and an 18-microhenry inductor at 3.505 MHz?
B. Point 3
E5C12 (A)
Which point on Figure E5-1 best represents the impedance of a series circuit consisting of a 300-ohm resistor and a 19-picofarad capacitor at 21.200 MHz?
A. Point 1
E5D RF effects in components and circuits: skin effect; real and reactive power; electrical length of conductors
E5D01 (A)
What is the result of conductor skin effect?
A. Resistance increases as frequency increases because RF current flows closer to the surface
E5D02 (B)
Why is it important to keep lead lengths short for components used in circuits for VHF and above?
B. To minimize inductive reactance
E5D03 (C)
What is the phase relationship between current and voltage for reactive power?
C. They are 90 degrees out of phase
E5D04 (B)
Why are short connections used at microwave frequencies?
B. To reduce phase shift along the connection
E5D05 (C)
What parasitic characteristic causes electrolytic capacitors to be unsuitable for use at RF?
C. Inductance
E5D06 (D)
What parasitic characteristic creates an inductor’s self-resonance?
D. Inter-turn capacitance
E5D07 (B)
What combines to create the self-resonance of a component?
B. The component’s nominal and parasitic reactance
E5D08 (D)
What is the primary cause of loss in film capacitors at RF?
D. Skin effect
E5D09 (B)
What happens to reactive power in ideal inductors and capacitors?
B. Energy is stored in magnetic or electric fields, but power is not dissipated
E5D10 (D)
As a conductor’s diameter increases, what is the effect on its electrical length?
D. It increases
E5D11 (B)
How much real power is consumed in a circuit consisting of a 100-ohm resistor in series with a 100-ohm inductive reactance drawing 1 ampere?
B. 100 watts
E5D12 (D)
What is reactive power?
D. Wattless, nonproductive power
SUBELEMENT E6 – CIRCUIT COMPONENTS [6 Exam Questions – 6 Groups]
E6A Semiconductor materials and devices: semiconductor materials; bipolar junction transistors; operation and types of field-effect transistors
E6A01 (C)
In what application is gallium arsenide used as a semiconductor material?
C. In microwave circuits
E6A02 (A)
Which of the following semiconductor materials contains excess free electrons?
A. N-type
E6A03 (C)
Why does a PN-junction diode not conduct current when reverse biased?
C. Holes in P-type material and electrons in the N-type material are separated by the applied voltage, widening the depletion region
E6A04 (C)
What is the name given to an impurity atom that adds holes to a semiconductor crystal structure?
C. Acceptor impurity
E6A05 (C)
How does DC input impedance at the gate of a field-effect transistor (FET) compare with that of a bipolar transistor?
C. An FET has higher input impedance
E6A06 (B)
What is the beta of a bipolar junction transistor?
B. The change in collector current with respect to the change in base current
E6A07 (D)
Which of the following indicates that a silicon NPN junction transistor is biased on?
D. Base-to-emitter voltage of approximately 0.6 volts to 0.7 volts
E6A08 (D)
What is the term for the frequency at which the grounded-base current gain of a bipolar junction transistor has decreased to 0.7 of the gain obtainable at 1 kHz?
D. Alpha cutoff frequency
E6A09 (A)
What is a depletion-mode field-effect transistor (FET)?
A. An FET that exhibits a current flow between source and drain when no gate voltage is applied
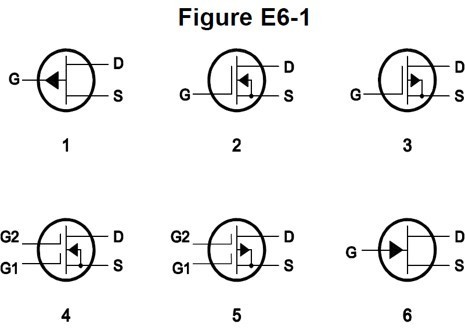
E6A10 (B)
In Figure E6-1, which is the schematic symbol for an N-channel dual-gate MOSFET?
B. 4
E6A11 (A)
In Figure E6-1, which is the schematic symbol for a P-channel junction FET?
A. 1
E6A12 (D)
What is the purpose of connecting Zener diodes between a MOSFET gate and its source or drain?
D. To protect the gate from static damage
E6B Diodes
E6B01 (B)
What is the most useful characteristic of a Zener diode?
B. A constant voltage drop under conditions of varying current
E6B02 (D)
Which characteristic of a Schottky diode makes it a better choice than a silicon junction diode for use as a power supply rectifier?
D. Lower forward voltage drop
E6B03 (B)
What property of an LED’s semiconductor material determines its forward voltage drop?
B. Band gap
E6B04 (A)
What type of semiconductor device is designed for use as a voltage-controlled capacitor?
A. Varactor diode
E6B05 (D)
What characteristic of a PIN diode makes it useful as an RF switch?
D. Low junction capacitance
E6B06 (D)
Which of the following is a common use of a Schottky diode?
D. As a VHF/UHF mixer or detector
E6B07 (B)
What causes a junction diode to fail from excessive current?
B. Excessive junction temperature
E6B08 (A)
Which of the following is a Schottky barrier diode?
A. Metal-semiconductor junction
E6B09 (C)
What is a common use for point-contact diodes?
C. As an RF detector
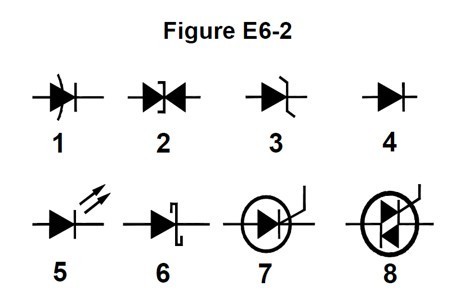
E6B10 (B)
In Figure E6-2, which is the schematic symbol for a Schottky diode?
B. 6
E6B11 (A)
What is used to control the attenuation of RF signals by a PIN diode?
A. Forward DC bias current
E6C Digital ICs: families of digital ICs; gates; programmable logic devices
E6C01 (A)
What is the function of hysteresis in a comparator?
A. To prevent input noise from causing unstable output signals
E6C02 (B)
What happens when the level of a comparator’s input signal crosses the threshold voltage?
B. The comparator changes its output state
E6C03 (A)
What is tri-state logic?
A. Logic devices with 0, 1, and high-impedance output states
E6C04 (C)
Which of the following is an advantage of BiCMOS logic?
C. It has the high input impedance of CMOS and the low output impedance of bipolar transistors
E6C05 (D)
Which of the following digital logic families has the lowest power consumption?
D. CMOS
E6C06 (C)
Why do CMOS digital integrated circuits have high immunity to noise on the input signal or power supply?
C. The input switching threshold is about half the power supply voltage
E6C07 (B)
What best describes a pull-up or pull-down resistor?
B. A resistor connected to the positive or negative supply used to establish a voltage when an input or output is an open circuit
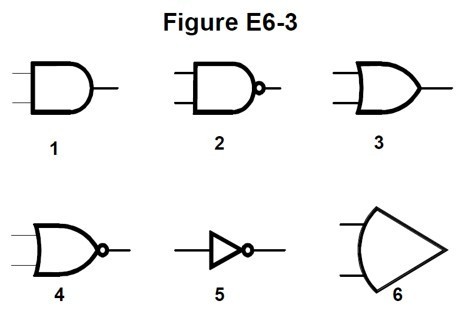
E6C08 (B)
In Figure E6-3, which is the schematic symbol for a NAND gate?
B. 2
E6C09 (B)
What is used to design the configuration of a field-programmable gate array (FPGA)?
B. Hardware description language (HDL)
E6C10 (D)
In Figure E6-3, which is the schematic symbol for a NOR gate?
D. 4
E6C11 (C)
In Figure E6-3, which is the schematic symbol for the NOT operation (inversion)?
C. 5
E6D Inductors and piezoelectricity: permeability, core material and configuration; transformers; piezoelectric devices
E6D01 (C)
What is piezoelectricity?
C. A characteristic of materials that generate a voltage when stressed and that flex when a voltage is applied
E6D02 (A)
What is the equivalent circuit of a quartz crystal?
A. Series RLC in parallel with a shunt C representing electrode and stray capacitance
E6D03 (A)
Which of the following is an aspect of the piezoelectric effect?
A. Mechanical deformation of material due to the application of a voltage
E6D04 (B)
Why are cores of inductors and transformers sometimes constructed of thin layers?
B. To reduce power loss from eddy currents in the core
E6D05 (C)
How do ferrite and powdered iron compare for use in an inductor core?
C. Ferrite cores generally require fewer turns to produce a given inductance value
E6D06 (D)
What core material property determines the inductance of an inductor?
D. Permeability
E6D07 (D)
What is the current that flows in the primary winding of a transformer when there is no load on the secondary winding?
D. Magnetizing current
E6D08 (B)
Which of the following materials has the highest temperature stability of its magnetic characteristics?
B. Powdered iron
E6D09 (C)
What devices are commonly used as VHF and UHF parasitic suppressors at the input and output terminals of a transistor HF amplifier?
C. Ferrite beads
E6D10 (A)
What is a primary advantage of using a toroidal core instead of a solenoidal core in an inductor?
A. Toroidal cores confine most of the magnetic field within the core material
E6D11 (B)
Which type of core material decreases inductance when inserted into a coil?
B. Brass
E6D12 (C)
What causes inductor saturation?
C. Operation at excessive magnetic flux
E6E Semiconductor materials and packages for RF use
E6E01 (B)
Why is gallium arsenide (GaAs) useful for semiconductor devices operating at UHF and higher frequencies?
B. Higher electron mobility
E6E02 (A)
Which of the following device packages is a through-hole type?
A. DIP
E6E03 (D)
Which of the following materials supports the highest frequency of operation when used in MMICs?
D. Gallium nitride
E6E04 (A)
Which is the most common input and output impedance of MMICs?
A. 50 ohms
E6E05 (A)
Which of the following noise figure values is typical of a low-noise UHF preamplifier?
A. 0.5 dB
E6E06 (D)
What characteristics of MMICs make them a popular choice for VHF through microwave circuits?
D. Controlled gain, low noise figure, and constant input and output impedance over the specified frequency range
E6E07 (D)
What type of transmission line is often used for connections to MMICs?
D. Microstrip
E6E08 (C)
How is power supplied to the most common type of MMIC?
C. Through a resistor and/or RF choke connected to the amplifier output lead
E6E09 (D)
Which of the following component package types have the least parasitic effects at frequencies above the HF range?
D. Surface mount
E6E10 (D)
What advantage does surface-mount technology offer at RF compared to using through-hole components?
A. Smaller circuit area
B. Shorter circuit board traces
C. Components have less parasitic inductance and capacitance
D. All these choices are correct
E6E11 (D)
What is a characteristic of DIP packaging used for integrated circuits?
D. Two rows of connecting pins on opposite sides of package (dual in-line package)
E6E12 (C)
Why are DIP through-hole package ICs not typically used at UHF and higher frequencies?
C. Excessive lead length
E6F Electro-optical technology: photoconductivity; photovoltaic devices; optical sensors and encoders; optically isolated switching
E6F01 (C)
What absorbs the energy from light falling on a photovoltaic cell?
C. Electrons
E6F02 (A)
What happens to photoconductive material when light shines on it?
A. Resistance decreases
E6F03 (D)
What is the most common configuration of an optoisolator or optocoupler?
D. An LED and a phototransistor
E6F04 (B)
What is the photovoltaic effect?
B. The conversion of light to electrical energy
E6F05 (A)
Which of the following describes an optical shaft encoder?
A. A device that detects rotation by interrupting a light source with a patterned wheel
E6F06 (C)
Which of these materials is most commonly used to create photoconductive devices?
C. Crystalline semiconductor
E6F07 (B)
What is a solid-state relay?
B. A device that uses semiconductors to implement the functions of an electromechanical relay
E6F08 (C)
Why are optoisolators often used in conjunction with solid-state circuits that control 120 VAC circuits?
C. Optoisolators provide an electrical isolation between a control circuit and the circuit being switched
E6F09 (D)
What is the efficiency of a photovoltaic cell?
D. The relative fraction of light that is converted to current
E6F10 (B)
What is the most common material used in power-generating photovoltaic cells?
B. Silicon
E6F11 (A)
What is the approximate open-circuit voltage produced by a fully illuminated silicon photovoltaic cell?
A. 0.5 volts
SUBELEMENT E7 – PRACTICAL CIRCUITS [8 Exam Questions – 8 Groups]
E7A Digital circuits: digital circuit principles and logic circuits; classes of logic elements; positive and negative logic; frequency dividers; truth tables
E7A01 (C)
Which circuit is bistable?
C. A flip-flop
E7A02 (A)
What is the function of a decade counter?
A. It produces one output pulse for every 10 input pulses
E7A03 (B)
Which of the following can divide the frequency of a pulse train by 2?
B. A flip-flop
E7A04 (A)
How many flip-flops are required to divide a signal frequency by 16?
A. 4
E7A05 (D)
Which of the following circuits continuously alternates between two states without an external clock signal?
D. Astable multivibrator
E7A06 (A)
What is a characteristic of a monostable multivibrator?
A. It switches temporarily to an alternate state for a set time
E7A07 (D)
What logical operation does a NAND gate perform?
D. It produces a 0 at its output only if all inputs are 1
E7A08 (A)
What logical operation does an OR gate perform?
A. It produces a 1 at its output if any input is 1
E7A09 (C)
What logical operation is performed by a two-input exclusive NOR gate?
C. It produces a 0 at its output if one and only one of its inputs is 1
E7A10 (B)
What is a truth table?
B. A list of inputs and corresponding outputs for a digital device
E7A11 (B)
What does “positive logic” mean in reference to logic devices?
B. High voltage represents a 1, low voltage a 0
E7B Amplifiers: class of operation; vacuum tube and solid-state circuits; distortion and intermodulation; spurious and parasitic suppression; switching-type amplifiers
E7B01 (A)
For what portion of the signal cycle does each active element in a push-pull, Class AB amplifier conduct?
A. More than 180 degrees but less than 360 degrees
E7B02 (A)
What is a Class D amplifier?
A. An amplifier that uses switching technology to achieve high efficiency
E7B03 (A)
What circuit is required at the output of an RF switching amplifier?
A. A filter to remove harmonic content
E7B04 (A)
What is the operating point of a Class A common emitter amplifier?
A. Approximately halfway between saturation and cutoff
E7B05 (C)
What can be done to prevent unwanted oscillations in an RF power amplifier?
C. Install parasitic suppressors and/or neutralize the stage
E7B06 (B)
What is a characteristic of a grounded-grid amplifier?
B. Low input impedance
E7B07 (D)
Which of the following is the likely result of using a Class C amplifier to amplify a single-sideband phone signal?
D. Signal distortion and excessive bandwidth
E7B08 (B)
Why are switching amplifiers more efficient than linear amplifiers?
B. The switching device is at saturation or cutoff most of the time
E7B09 (D)
What is characteristic of an emitter follower (or common collector) amplifier?
D. Input and output signals in-phase
E7B10 (B)
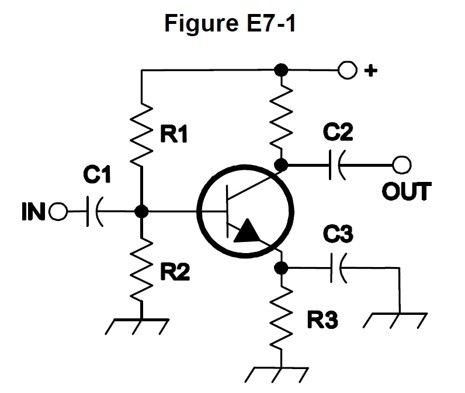
In Figure E7-1, what is the purpose of R1 and R2?
B. Voltage divider bias
E7B11 (D)
In Figure E7-1, what is the purpose of R3?
D. Self bias
E7B12 (C)
What type of amplifier circuit is shown in Figure E7-1?
C. Common emitter
E7C Filters and matching networks: types of networks; types of filters; filter applications; filter characteristics; impedance matching
E7C01 (D)
How are the capacitors and inductors of a low-pass filter Pi-network arranged between the network’s input and output?
D. A capacitor is connected between the input and ground, another capacitor is connected between the output and ground, and an inductor is connected between the input and output
E7C02 (B)
What is the frequency response of a T-network with series capacitors and a shunt inductor?
B. High-pass
E7C03 (A)
What is the purpose of adding an inductor to a Pi-network to create a Pi-L-network?
A. Greater harmonic suppression
E7C04 (C)
How does an impedance-matching circuit transform a complex impedance to a resistive impedance?
C. It cancels the reactive part of the impedance and changes the resistive part to the desired value
E7C05 (D)
Which filter type has ripple in the passband and a sharp cutoff?
D. A Chebyshev filter
E7C06 (C)
What are the characteristics of an elliptical filter?
C. Extremely sharp cutoff with one or more notches in the stop band
E7C07 (B)
Which describes a Pi-L network?
B. A Pi-network with an additional output series inductor
E7C08 (B)
Which of the following is most frequently used as a band-pass or notch filter in VHF and UHF transceivers?
B. A helical filter
E7C09 (D)
What is a crystal lattice filter?
D. A filter for low-level signals made using quartz crystals
E7C10 (B)
Which of the following filters is used in a 2-meter band repeater duplexer?
B. A cavity filter
E7C11 (C)
Which of the following measures a filter’s ability to reject signals in adjacent channels?
C. Shape factor
E7D Power supplies and voltage regulators; solar array charge controllers
E7D01 (D)
How does a linear electronic voltage regulator work?
D. The conduction of a control element is varied to maintain a constant output voltage
E7D02 (B)
How does a switchmode voltage regulator work?
B. By varying the duty cycle of pulses input to a filter
E7D03 (A)
What device is used as a stable voltage reference?
A. A Zener diode
E7D04 (B)
Which of the following describes a three-terminal voltage regulator?
B. A series regulator
E7D05 (D)
Which of the following types of linear voltage regulator operates by loading the unregulated voltage source?
D. A shunt regulator
E7D06 (C)
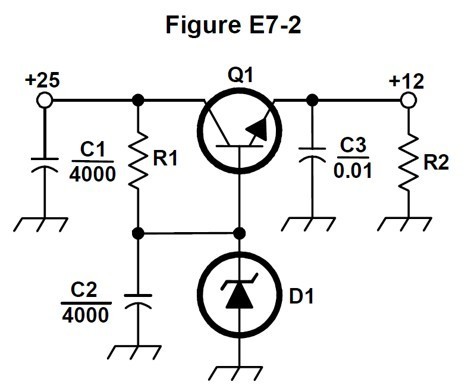
What is the purpose of Q1 in the circuit shown in Figure E7-2?
C. It controls the current to keep the output voltage constant
E7D07 (A)
What is the purpose of C2 in the circuit shown in Figure E7-2?
A. It bypasses rectifier output ripple around D1
E7D08 (C)
What type of circuit is shown in Figure E7-2?
C. Linear voltage regulator
E7D09 (C)
How is battery operating time calculated?
C. Capacity in amp-hours divided by average current
E7D10 (C)
Why is a switching type power supply less expensive and lighter than an equivalent linear power supply?
C. The high frequency inverter design uses much smaller transformers and filter components for an equivalent power output
E7D11 (D)
What is the purpose of an inverter connected to a solar panel output?
D. Convert the panel’s output from DC to AC
E7D12 (C)
What is the dropout voltage of a linear voltage regulator?
C. Minimum input-to-output voltage required to maintain regulation
E7D13 (C)
Which of the following calculates power dissipated by a series linear voltage regulator?
C. Voltage difference from input to output multiplied by output current
E7D14 (D)
What is the purpose of connecting equal-value resistors across power supply filter capacitors connected in series?
A. Equalize the voltage across each capacitor
B. Discharge the capacitors when voltage is removed
C. Provide a minimum load on the supply
D. All these choices are correct
E7D15 (D)
What is the purpose of a step-start circuit in a high-voltage power supply?
D. To allow the filter capacitors to charge gradually
E7E Modulation and demodulation: reactance, phase, and balanced modulators; detectors; mixers
E7E01 (B)
Which of the following can be used to generate FM phone signals?
B. Reactance modulation of a local oscillator
E7E02 (D)
What is the function of a reactance modulator?
D. Produce PM or FM signals by varying a capacitance
E7E03 (D)
What is a frequency discriminator?
D. A circuit for detecting FM signals
E7E04 (A)
What is one way to produce a single-sideband phone signal?
A. Use a balanced modulator followed by a filter
E7E05 (D)
What is added to an FM speech channel to boost the higher audio frequencies?
D. A pre-emphasis network
E7E06 (A)
Why is de-emphasis used in FM communications receivers?
A. For compatibility with transmitters using phase modulation
E7E07 (B)
What is meant by the term “baseband” in radio communications?
B. The frequency range occupied by a message signal prior to modulation
E7E08 (C)
What are the principal frequencies that appear at the output of a mixer?
C. The two input frequencies along with their sum and difference frequencies
E7E09 (A)
What occurs when the input signal levels to a mixer are too high?
A. Spurious mixer products are generated
E7E10 (A)
How does a diode envelope detector function?
A. By rectification and filtering of RF signals
E7E11 (C)
Which type of detector is used for demodulating SSB signals?
C. Product detector
E7F Software defined radio fundamentals: digital signal processing (DSP) filtering, modulation, and demodulation; analog-digital conversion; digital filters
E7F01 (C)
What is meant by “direct sampling” in software defined radios?
C. Incoming RF is digitized by an analog-to-digital converter without being mixed with a local oscillator signal
E7F02 (A)
What kind of digital signal processing audio filter is used to remove unwanted noise from a received SSB signal?
A. An adaptive filter
E7F03 (C)
What type of digital signal processing filter is used to generate an SSB signal?
C. A Hilbert-transform filter
E7F04 (D)
Which method generates an SSB signal using digital signal processing?
D. Signals are combined in quadrature phase relationship
E7F05 (B)
How frequently must an analog signal be sampled to be accurately reproduced?
B. At least twice the rate of the highest frequency component of the signal
E7F06 (D)
What is the minimum number of bits required to sample a signal with a range of 1 volt at a resolution of 1 millivolt?
D. 10 bits
E7F07 (C)
What function is performed by a Fast Fourier Transform?
C. Converting signals from the time domain to the frequency domain
E7F08 (B)
What is the function of decimation?
B. Reducing the effective sample rate by removing samples
E7F09 (A)
Why is an anti-aliasing filter required in a decimator?
A. It removes high-frequency signal components that would otherwise be reproduced as lower frequency components
E7F10 (A)
What aspect of receiver analog-to-digital conversion determines the maximum receive bandwidth of a direct-sampling software defined radio (SDR)?
A. Sample rate
E7F11 (B)
What sets the minimum detectable signal level for a direct-sampling software defined receiver in the absence of atmospheric or thermal noise?
B. Reference voltage level and sample width in bits
E7F12 (A)
Which of the following is generally true of Finite Impulse Response (FIR) filters?
A. FIR filters can delay all frequency components of the signal by the same amount
E7F13 (D)
What is the function of taps in a digital signal processing filter?
D. Provide incremental signal delays for filter algorithms
E7F14 (B)
Which of the following would allow a digital signal processing filter to create a sharper filter response?
B. More taps
E7G Operational amplifiers: characteristics and applications
E7G01 (A)
What is the typical output impedance of an op-amp?
A. Very low
E7G02 (B)
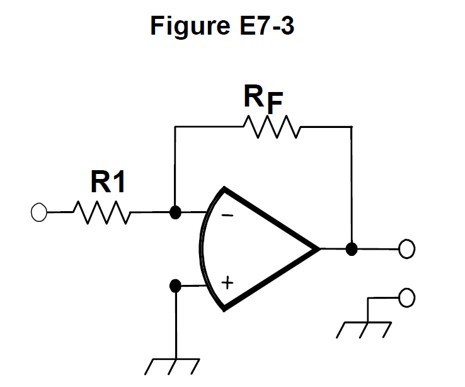
What is the frequency response of the circuit in E7-3 if a capacitor is added across the feedback resistor?
B. Low-pass filter
E7G03 (D)
What is the typical input impedance of an op-amp?
D. Very high
E7G04 (C)
What is meant by the term “op-amp input offset voltage”?
C. The differential input voltage needed to bring the open loop output voltage to zero
E7G05 (A)
How can unwanted ringing and audio instability be prevented in an op-amp audio filter?
A. Restrict both gain and Q
E7G06 (B)
What is the gain-bandwidth of an operational amplifier?
B. The frequency at which the open-loop gain of the amplifier equals one
E7G07 (C)
What voltage gain can be expected from the circuit in Figure E7-3 when R1 is 10 ohms and RF is 470 ohms?
C. 47
E7G08 (D)
How does the gain of an ideal operational amplifier vary with frequency?
D. It does not vary with frequency
E7G09 (D)
What will be the output voltage of the circuit shown in Figure E7-3 if R1 is 1,000 ohms, RF is 10,000 ohms, and 0.23 volts DC is applied to the input?
D. -2.3 volts
E7G10 (C)
What absolute voltage gain can be expected from the circuit in Figure E7-3 when R1 is 1,800 ohms and RF is 68 kilohms?
C. 38
E7G11 (B)
What absolute voltage gain can be expected from the circuit in Figure E7-3 when R1 is 3,300 ohms and RF is 47 kilohms?
B. 14
E7G12 (A)
What is an operational amplifier?
A. A high-gain, direct-coupled differential amplifier with very high input impedance and very low output impedance
E7H Oscillators and signal sources: types of oscillators; synthesizers and phase-locked loops; direct digital synthesizers; stabilizing thermal drift; microphonics; high-accuracy oscillators
E7H01 (D)
What are three common oscillator circuits?
D. Colpitts, Hartley, and Pierce
E7H02 (C)
What is a microphonic?
C. Changes in oscillator frequency caused by mechanical vibration
E7H03 (C)
What is a phase-locked loop?
C. An electronic servo loop consisting of a phase detector, a low-pass filter, a voltage-controlled oscillator, and a stable reference oscillator
E7H04 (C)
How is positive feedback supplied in a Colpitts oscillator?
C. Through a capacitive divider
E7H05 (D)
How is positive feedback supplied in a Pierce oscillator?
D. Through a quartz crystal
E7H06 (B)
Which of these functions can be performed by a phase-locked loop?
B. Frequency synthesis and FM demodulation
E7H07 (D)
How can an oscillator’s microphonic responses be reduced?
D. Mechanically isolate the oscillator circuitry from its enclosure
E7H08 (A)
Which of the following components can be used to reduce thermal drift in crystal oscillators?
A. NP0 capacitors
E7H09 (A)
What type of frequency synthesizer circuit uses a phase accumulator, lookup table, digital-to-analog converter, and a low-pass anti-alias filter?
A. A direct digital synthesizer
E7H10 (B)
What information is contained in the lookup table of a direct digital synthesizer (DDS)?
B. Amplitude values that represent the desired waveform
E7H11 (C)
What are the major spectral impurity components of direct digital synthesizers?
C. Spurious signals at discrete frequencies
E7H12 (B)
Which of the following ensures that a crystal oscillator operates on the frequency specified by the crystal manufacturer?
B. Provide the crystal with a specified parallel capacitance
E7H13 (D)
Which of the following is a technique for providing highly accurate and stable oscillators needed for microwave transmission and reception?
A. Use a GPS signal reference
B. Use a rubidium stabilized reference oscillator
C. Use a temperature-controlled high Q dielectric resonator
D. All these choices are correct
SUBELEMENT E8 – SIGNALS AND EMISSIONS [4 Exam Questions – 4 Groups]
E8A Fourier analysis; RMS measurements; average RF power and peak envelope power (PEP); analog/digital conversion
E8A01 (A)
What technique shows that a square wave is made up of a sine wave and its odd harmonics?
A. Fourier analysis
E8A02 (A)
Which of the following is a type of analog-to-digital conversion?
A. Successive approximation
E8A03 (B)
Which of the following describes a signal in the time domain?
B. Amplitude at different times
E8A04 (B)
What is “dither” with respect to analog-to-digital converters?
B. A small amount of noise added to the input signal to reduce quantization noise
E8A05 (D)
What is the benefit of making voltage measurements with a true-RMS calculating meter?
D. RMS is measured for both sinusoidal and non-sinusoidal signals
E8A06 (A)
What is the approximate ratio of PEP-to-average power in an unprocessed single-sideband phone signal?
A. 2.5 to 1
E8A07 (B)
What determines the PEP-to-average power ratio of an unprocessed single-sideband phone signal?
B. Speech characteristics
E8A08 (C)
Why are direct or flash conversion analog-to-digital converters used for a software defined radio?
C. Very high speed allows digitizing high frequencies
E8A09 (D)
How many different input levels can be encoded by an analog-to-digital converter with 8-bit resolution?
D. 256
E8A10 (C)
What is the purpose of a low-pass filter used at the output of a digital-to-analog converter?
C. Remove spurious sampling artifacts from the output signal
E8A11 (A)
Which of the following is a measure of the quality of an analog-to-digital converter?
A. Total harmonic distortion
E8B Modulation and demodulation: modulation methods; modulation index and deviation ratio; frequency- and time-division multiplexing; orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM)
E8B01 (A)
What is the modulation index of an FM signal?
A. The ratio of frequency deviation to modulating signal frequency
E8B02 (D)
How does the modulation index of a phase-modulated emission vary with RF carrier frequency?
D. It does not depend on the RF carrier frequency
E8B03 (A)
What is the modulation index of an FM phone signal having a maximum frequency deviation of 3000 Hz either side of the carrier frequency if the highest modulating frequency is 1000 Hz?
A. 3
E8B04 (B)
What is the modulation index of an FM phone signal having a maximum carrier deviation of plus or minus 6 kHz if the highest modulating frequency is 2 kHz?
B. 3
E8B05 (D)
What is the deviation ratio of an FM phone signal having a maximum frequency swing of plus or minus 5 kHz if the highest modulation frequency is 3 kHz?
D. 1.67
E8B06 (A)
What is the deviation ratio of an FM phone signal having a maximum frequency swing of plus or minus 7.5 kHz if the highest modulation frequency is 3.5 kHz?
A. 2.14
E8B07 (A)
Orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) is a technique used for which types of amateur communication?
A. Digital modes
E8B08 (D)
What describes orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM)?
D. A digital modulation technique using subcarriers at frequencies chosen to avoid intersymbol interference
E8B09 (B)
What is deviation ratio?
B. The ratio of the maximum carrier frequency deviation to the highest audio modulating frequency
E8B10 (B)
What is frequency division multiplexing (FDM)?
B. Dividing the transmitted signal into separate frequency bands that each carry a different data stream
E8B11 (B)
What is digital time division multiplexing?
B. Two or more signals are arranged to share discrete time slots of a data transmission
E8C Digital signals: digital communication modes; information rate vs. bandwidth; error correction; constellation diagrams
E8C01 (B)
What is Quadrature Amplitude Modulation or QAM?
B. Transmission of data by modulating the amplitude of two carriers of the same frequency but 90 degrees out of phase
E8C02 (C)
What is the definition of symbol rate in a digital transmission?
C. The rate at which the waveform changes to convey information
E8C03 (A)
Why should the phase of a PSK signal be changed at the zero crossing of the RF signal?
A. To minimize bandwidth
E8C04 (C)
What technique minimizes the bandwidth of a PSK31 signal?
C. Use of sinusoidal data pulses
E8C05 (C)
What is the approximate bandwidth of a 13-WPM International Morse Code transmission?
C. 52 Hz
E8C06 (B)
What is the bandwidth of an FT8 signal?
B. 50 Hz
E8C07 (A)
What is the bandwidth of a 4,800-Hz frequency shift, 9,600-baud ASCII FM transmission?
A. 15.36 kHz
E8C08 (D)
How does ARQ accomplish error correction?
D. If errors are detected, a retransmission is requested
E8C09 (D)
Which digital code allows only one bit to change between sequential code values?
D. Gray code
E8C10 (C)
How can data rate be increased without increasing bandwidth?
C. Using a more efficient digital code
E8C11 (A)
What is the relationship between symbol rate and baud?
A. They are the same
E8C12 (C)
What factors affect the bandwidth of a transmitted CW signal?
C. Keying speed and shape factor (rise and fall time)
E8C13 (B)
What is described by the constellation diagram of a QAM or QPSK signal?
B. The possible phase and amplitude states for each symbol
E8C14 (C)
What type of addresses do nodes have in a mesh network?
C. Internet Protocol (IP)
E8C15 (C)
What technique do individual nodes use to form a mesh network?
C. Discovery and link establishment protocols
E8D Keying defects and overmodulation of digital signals; digital codes; spread spectrum
E8D01 (A)
Why are received spread spectrum signals resistant to interference?
A. Signals not using the spread spectrum algorithm are suppressed in the receiver
E8D02 (B)
What spread spectrum communications technique uses a high-speed binary bit stream to shift the phase of an RF carrier?
B. Direct sequence
E8D03 (D)
Which describes spread spectrum frequency hopping?
D. Rapidly varying the frequency of a transmitted signal according to a pseudorandom sequence
E8D04 (C)
What is the primary effect of extremely short rise or fall time on a CW signal?
C. The generation of key clicks
E8D05 (A)
What is the most common method of reducing key clicks?
A. Increase keying waveform rise and fall times
E8D06 (D)
What is the advantage of including parity bits in ASCII characters?
D. Some types of errors can be detected
E8D07 (D)
What is a common cause of overmodulation of AFSK signals?
D. Excessive transmit audio levels
E8D08 (D)
What parameter evaluates distortion of an AFSK signal caused by excessive input audio levels?
D. Intermodulation Distortion (IMD)
E8D09 (D)
What is considered an acceptable maximum IMD level for an idling PSK signal?
D. -30 dB
E8D10 (B)
What are some of the differences between the Baudot digital code and ASCII?
B. Baudot uses 5 data bits per character, ASCII uses 7 or 8; Baudot uses 2 characters as letters/figures shift codes, ASCII has no letters/figures shift code
E8D11 (C)
What is one advantage of using ASCII code for data communications?
C. It is possible to transmit both uppercase and lowercase text
SUBELEMENT E9 – ANTENNAS AND TRANSMISSION LINES [8 Exam Questions – 8 Groups]
E9A Basic antenna parameters: radiation resistance, gain, beamwidth, efficiency; effective radiated power (ERP) and effective isotropic radiated power (EIRP)
E9A01 (C)
What is an isotropic radiator?
C. A hypothetical, lossless antenna having equal radiation intensity in all directions used as a reference for antenna gain
E9A02 (D)
What is the effective radiated power (ERP) of a repeater station with 150 watts transmitter power output, 2 dB feed line loss, 2.2 dB duplexer loss, and 7 dBd antenna gain?
D. 286 watts
E9A03 (C)
What term describing total radiated power takes into account all gains and losses?
C. Effective radiated power
E9A04 (B)
Which of the following factors affect the feed point impedance of an antenna?
B. Antenna height
E9A05 (D)
What does the term “ground gain” mean?
D. An increase in signal strength from ground reflections in the environment of the antenna
E9A06 (A)
What is the effective radiated power (ERP) of a repeater station with 200 watts transmitter power output, 4 dB feed line loss, 3.2 dB duplexer loss, 0.8 dB circulator loss, and 10 dBd antenna gain?
A. 317 watts
E9A07 (B)
What is the effective isotropic radiated power (EIRP) of a repeater station with 200 watts transmitter power output, 2 dB feed line loss, 2.8 dB duplexer loss, 1.2 dB circulator loss, and 7 dBi antenna gain?
B. 252 watts
E9A08 (A)
Which frequency band has the smallest first Fresnel zone?
A. 5.8 GHz
E9A09 (B)
What is antenna efficiency?
B. Radiation resistance divided by total resistance
E9A10 (A)
Which of the following improves the efficiency of a ground-mounted quarter-wave vertical antenna?
A. Installing a ground radial system
E9A11 (C)
Which of the following determines ground losses for a ground-mounted vertical antenna operating on HF?
C. Soil conductivity
E9A12 (A)
How much gain does an antenna have compared to a half-wavelength dipole if it has 6 dB gain over an isotropic radiator?
A. 3.85 dB
E9B Antenna patterns and designs: azimuth and elevation patterns; gain as a function of pattern; antenna modeling
E9B01 (B)
What is the 3 dB beamwidth of the antenna radiation pattern shown in Figure E9-1?
B. 50 degrees
E9B02 (D)
What is the front-to-back ratio of the antenna radiation pattern shown in Figure E9-1?
D. 18 dB
E9B03 (D)
What is the front-to-side ratio of the antenna radiation pattern shown in Figure E9-1?
D. 14 dB
E9B04 (B)
What is the front-to-back ratio of the radiation pattern shown in Figure E9-2?
B. 28 dB
E9B05 (A)
What type of antenna pattern is shown in Figure E9-2?
A. Elevation
E9B06 (C)
What is the elevation angle of peak response in the antenna radiation pattern shown in Figure E9-2?
C. 7.5 degrees
E9B07 (C)
What is the difference in radiated power between a lossless antenna with gain and an isotropic radiator driven by the same power?
C. They are the same
E9B08 (D)
What is the far field of an antenna?
D. The region where the shape of the radiation pattern no longer varies with distance
E9B09 (B)
What type of analysis is commonly used for modeling antennas?
B. Method of Moments
E9B10 (A)
What is the principle of a Method of Moments analysis?
A. A wire is modeled as a series of segments, each having a uniform value of current
E9B11 (C)
What is a disadvantage of decreasing the number of wire segments in an antenna model below 10 segments per half-wavelength?
C. The computed feed point impedance may be incorrect
E9C Practical wire antennas; folded dipoles; phased arrays; effects of ground near antennas
E9C01 (D)
What type of radiation pattern is created by two 1/4-wavelength vertical antennas spaced 1/2-wavelength apart and fed 180 degrees out of phase?
D. A figure-eight oriented along the axis of the array
E9C02 (A)
What type of radiation pattern is created by two 1/4-wavelength vertical antennas spaced 1/4-wavelength apart and fed 90 degrees out of phase?
A. Cardioid
E9C03 (C)
What type of radiation pattern is created by two 1/4-wavelength vertical antennas spaced 1/2-wavelength apart and fed in phase?
C. A figure-eight broadside to the axis of the array
E9C04 (B)
What happens to the radiation pattern of an unterminated long wire antenna as the wire length is increased?
B. Additional lobes form with major lobes increasingly aligned with the axis of the antenna
E9C05 (A)
What is the purpose of feeding an off-center-fed dipole (OCFD) between the center and one end instead of at the midpoint?
A. To create a similar feed point impedance on multiple bands
E9C06 (B)
What is the effect of adding a terminating resistor to a rhombic or long-wire antenna?
B. It changes the radiation pattern from bidirectional to unidirectional
E9C07 (A)
What is the approximate feed point impedance at the center of a two-wire half-wave folded dipole antenna?
A. 300 ohms
E9C08 (C)
What is a folded dipole antenna?
C. A half-wave dipole with an additional parallel wire connecting its two ends
E9C09 (A)
Which of the following describes a G5RV antenna?
A. A wire antenna center-fed through a specific length of open-wire line connected to a balun and coaxial feed line
E9C10 (B)
Which of the following describes a Zepp antenna?
B. An end-fed half-wavelength dipole
E9C11 (D)
How is the far-field elevation pattern of a vertically polarized antenna affected by being mounted over seawater versus soil?
D. Radiation at low angles increases
E9C12 (C)
Which of the following describes an extended double Zepp antenna?
C. A center-fed 1.25-wavelength dipole antenna
E9C13 (B)
How does the radiation pattern of a horizontally polarized antenna vary with increasing height above ground?
B. The takeoff angle of the lowest elevation lobe decreases
E9C14 (B)
How does the radiation pattern of a horizontally-polarized antenna mounted above a long slope compare with the same antenna mounted above flat ground?
B. The main lobe takeoff angle decreases in the downhill direction
E9D Yagi antennas; parabolic reflectors; feed point impedance and loading of electrically short antennas; antenna Q; RF grounding
E9D01 (D)
How much does the gain of an ideal parabolic reflector antenna increase when the operating frequency is doubled?
D. 6 dB
E9D02 (C)
How can two linearly polarized Yagi antennas be used to produce circular polarization?
C. Arrange two Yagis on the same axis and perpendicular to each other with the driven elements at the same point on the boom and fed 90 degrees out of phase
E9D03 (A)
What is the most efficient location for a loading coil on an electrically short whip?
A. Near the center of the vertical radiator
E9D04 (C)
Why should antenna loading coils have a high ratio of reactance to resistance?
C. To maximize efficiency
E9D05 (D)
Approximately how long is a Yagi’s driven element?
D. 1/2 wavelength
E9D06 (B)
What happens to SWR bandwidth when one or more loading coils are used to resonate an electrically short antenna?
B. It is decreased
E9D07 (D)
What is an advantage of top loading an electrically short HF vertical antenna?
D. Improved radiation efficiency
E9D08 (B)
What happens as the Q of an antenna increases?
B. SWR bandwidth decreases
E9D09 (D)
What is the function of a loading coil in an electrically short antenna?
D. To resonate the antenna by cancelling the capacitive reactance
E9D10 (B)
How does radiation resistance of a base-fed whip antenna change below its resonant frequency?
B. Radiation resistance decreases
E9D11 (D)
Why do most two-element Yagis with normal spacing have a reflector instead of a director?
D. Higher gain
E9D12 (C)
What is the purpose of making a Yagi’s parasitic elements either longer or shorter than resonance?
C. Control of phase shift
E9E Impedance matching: matching antennas to feed lines; phasing lines; power dividers
E9E01 (B)
Which matching system for Yagi antennas requires the driven element to be insulated from the boom?
B. Beta or hairpin
E9E02 (A)
What antenna matching system matches coaxial cable to an antenna by connecting the shield to the center of the antenna and the conductor a fraction of a wavelength to one side?
A. Gamma match
E9E03 (D)
What matching system uses a short length of transmission line connected in parallel with the feed line at or near the feed point?
D. Stub match
E9E04 (B)
What is the purpose of the series capacitor in a gamma match?
B. To cancel unwanted inductive reactance
E9E05 (A)
What Yagi driven element feed point impedance is required to use a beta or hairpin matching system?
A. Capacitive (driven element electrically shorter than 1/2 wavelength)
E9E06 (C)
Which of these transmission line impedances would be suitable for constructing a quarter-wave Q-section for matching a 100-ohm feed point impedance to a 50-ohm transmission line?
C. 75 ohms
E9E07 (B)
What parameter describes the interaction of a load and transmission line?
B. Reflection coefficient
E9E08 (C)
What is a use for a Wilkinson divider?
C. To divide power equally between two 50-ohm loads while maintaining 50-ohm input impedance
E9E09 (C)
Which of the following is used to shunt feed a grounded tower at its base?
C. Gamma match
E9E11 (A)
What is the purpose of using multiple driven elements connected through phasing lines?
A. To control the antenna’s radiation pattern
E9F Transmission lines: characteristics of open and shorted feed lines; coax versus open wire; velocity factor; electrical length; coaxial cable dielectrics; microstrip
E9F01 (D)
What is the velocity factor of a transmission line?
D. The velocity of a wave in the transmission line divided by the velocity of light in a vacuum
E9F02 (C)
Which of the following has the biggest effect on the velocity factor of a transmission line?
C. The insulating dielectric material
E9F03 (D)
Why is the electrical length of a coaxial cable longer than its physical length?
D. Electromagnetic waves move more slowly in a coaxial cable than in air
E9F04 (B)
What impedance does a 1/2-wavelength transmission line present to an RF generator when the line is shorted at the far end?
B. Very low impedance
E9F05 (D)
What is microstrip?
D. Precision printed circuit conductors above a ground plane that provide constant impedance interconnects at microwave frequencies
E9F06 (C)
What is the approximate physical length of an air-insulated, parallel conductor transmission line that is electrically 1/2 wavelength long at 14.10 MHz?
C. 10.6 meters
E9F07 (A)
How does parallel conductor transmission line compare to coaxial cable with a plastic dielectric?
A. Lower loss
E9F08 (D)
Which of the following is a significant difference between foam dielectric coaxial cable and solid dielectric coaxial cable, assuming all other parameters are the same?
A. Foam dielectric coaxial cable has lower safe maximum operating voltage
B. Foam dielectric coaxial cable has lower loss per unit of length
C. Foam dielectric coaxial cable has higher velocity factor
D. All these choices are correct
E9F09 (A)
What impedance does a 1/4-wavelength transmission line present to an RF generator when the line is shorted at the far end?
A. Very high impedance
E9F10 (C)
What impedance does a 1/8-wavelength transmission line present to an RF generator when the line is shorted at the far end?
C. An inductive reactance
E9F11 (C)
What impedance does a 1/8-wavelength transmission line present to an RF generator when the line is open at the far end?
C. A capacitive reactance
E9F12 (D)
What impedance does a 1/4-wavelength transmission line present to an RF generator when the line is open at the far end?
D. Very low impedance
E9G The Smith chart
E9G01 (A)
Which of the following can be calculated using a Smith chart?
A. Impedance along transmission lines
E9G02 (B)
What type of coordinate system is used in a Smith chart?
B. Resistance circles and reactance arcs
E9G03 (C)
Which of the following is often determined using a Smith chart?
C. Impedance and SWR values in transmission lines
E9G04 (C)
What are the two families of circles and arcs that make up a Smith chart?
C. Resistance and reactance
E9G05 (A)
Which of the following is a common use for a Smith chart?
A. Determine the length and position of an impedance matching stub
E9G06 (B)
On the Smith chart shown in Figure E9-3, what is the name for the large outer circle on which the reactance arcs terminate?
B. Reactance axis
E9G07 (D)
On the Smith chart shown in Figure E9-3, what is the only straight line shown?
D. The resistance axis
E9G08 (C)
How is a Smith chart normalized?
C. Reassign the prime center’s impedance value
E9G09 (A)
What third family of circles is often added to a Smith chart during the process of designing impedance matching networks?
A. Constant-SWR circles
E9G10 (D)
What do the arcs on a Smith chart represent?
D. Points with constant reactance
E9G11 (B)
In what units are the wavelength scales on a Smith chart calibrated?
B. In fractions of transmission line electrical wavelength
E9H Receiving antennas: radio direction finding (RDF) techniques; Beverage antennas; single- and multiple-turn loops
E9H01 (D)
When constructing a Beverage antenna, which of the following factors should be included in the design to achieve good performance at the desired frequency?
D. It should be at least one wavelength long
E9H02 (A)
Which is generally true for 160- and 80-meter receiving antennas?
A. Atmospheric noise is so high that directivity is much more important than losses
E9H03 (D)
What is receiving directivity factor (RDF)?
D. Peak antenna gain compared to average gain over the hemisphere around and above the antenna
E9H04 (B)
What is the purpose of placing an electrostatic shield around a small-loop direction-finding antenna?
B. It eliminates unbalanced capacitive coupling to the antenna’s surroundings, improving the depth of its nulls
E9H05 (A)
What challenge is presented by a small wire-loop antenna for direction finding?
A. It has a bidirectional null pattern
E9H06 (D)
What indicates the correct value of terminating resistance for a Beverage antenna?
D. Minimum variation in SWR over the desired frequency range
E9H07 (B)
What is the function of a Beverage antenna’s termination resistor?
B. Absorb signals from the reverse direction
E9H08 (A)
What is the function of a sense antenna?
A. It modifies the pattern of a DF antenna to provide a null in only one direction
E9H09 (A)
What type of radiation pattern is created by a single-turn, terminated loop such as a pennant antenna?
A. Cardioid
E9H10 (C)
How can the output voltage of a multiple-turn receiving loop antenna be increased?
C. By increasing the number of turns and/or the area enclosed by the loop
E9H11 (B)
What feature of a cardioid pattern antenna makes it useful for direction-finding antennas?
B. A single null
SUBELEMENT E0 – SAFETY – [1 exam question – 1 group]
E0A Safety: RF radiation hazards; hazardous materials; grounding
E0A01 (B)
What is the primary function of an external earth connection or ground rod?
B. Lightning charge dissipation
E0A02 (B)
When evaluating RF exposure levels from your station at a neighbor’s home, what must you do?
B. Ensure signals from your station are less than the uncontrolled maximum permissible exposure (MPE) limits
E0A03 (C)
Over what range of frequencies are the FCC human body RF exposure limits most restrictive?
C. 30 – 300 MHz
E0A04 (C)
When evaluating a site with multiple transmitters operating at the same time, the operators and licensees of which transmitters are responsible for mitigating over-exposure situations?
C. Each transmitter that produces 5 percent or more of its MPE limit in areas where the total MPE limit is exceeded
E0A05 (B)
What hazard is created by operating at microwave frequencies?
B. The high gain antennas commonly used can result in high exposure levels
E0A06 (D)
Why are there separate electric (E) and magnetic (H) MPE limits at frequencies below 300 MHz?
A. The body reacts to electromagnetic radiation from both the E and H fields
B. Ground reflections and scattering cause the field strength to vary with location
C. E field and H field radiation intensity peaks can occur at different locations
D. All these choices are correct
E0A07 (B)
What is meant by “100% tie-off” regarding tower safety?
B. At least one lanyard attached to the tower at all times
E0A08 (C)
What does SAR measure?
C. The rate at which RF energy is absorbed by the body
E0A09 (C)
Which of the following types of equipment are exempt from RF exposure evaluations?
C. Hand-held transceivers sold before May 3, 2021
E0A10 (A)
When must an RF exposure evaluation be performed on an amateur station operating on 80 meters?
A. An evaluation must always be performed
E0A11 (D)
To what should lanyards be attached while climbing?
D. Tower legs
E0A12 (A)
Where should a shock-absorbing lanyard be attached to a tower when working above ground?
A. Above the climber’s head level